MOONS' stepper motor temperature rise test introduction
Stepper motors are widely used in motion control systems. Many users use stepper motors, and often the feedback stepper motor temperature rise is relatively high, why is this? How does MOONS' test the motor's temperature rise? 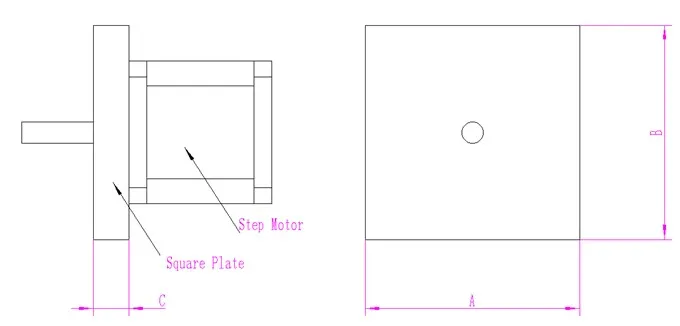
 ● Through the heat sink, attach the motor to the bracket. The shaded area between the bracket and the heat sink is a nylon heat shield. Please refer to the following figure:
● Through the heat sink, attach the motor to the bracket. The shaded area between the bracket and the heat sink is a nylon heat shield. Please refer to the following figure: 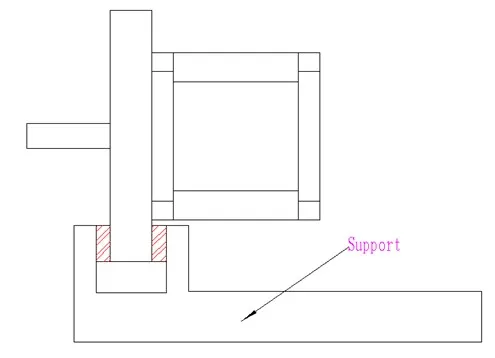 ● Test the motor surface temperature by placing the sensor on the motor surface, driving the motor, and recording the results.
● Test the motor surface temperature by placing the sensor on the motor surface, driving the motor, and recording the results.
First, why do stepper motors have a relatively high-temperature rise?
Any motor will heat up, but the range of temperature rise varies. Stepper motors have a core and coils wound around them. As the winding has resistance, it will cause loss when energized; if the current is not a standard DC or sine wave, harmonic losses will occur; the core's hysteresis eddy current is less than that in the alternating magnetic field. A motor's efficiency can be affected by damage manifested as heat. As a result of stepper motors' focus on positioning accuracy and torque output, their efficiency is relatively low, their current is generally large, and their harmonic components are high. As the frequency of the alternating current varies with rotational speed, the temperature rise of the stepping motor is relatively high.Second, what is a reasonable range of temperature rise for stepper motors?
There is a limit to the amount of temperature rise that can be tolerated by the motor, which is determined by its internal insulation level. The general insulation class of the stepper motor is ClassB, which means that only the internal temperature will not exceed 130 degrees, the motor will not be damaged, and the surface temperature will be below 90 degrees. Therefore, a stepper motor's surface temperature of 60 degrees is considered normal.Third, how does MOONS' test the motor's temperature rise?
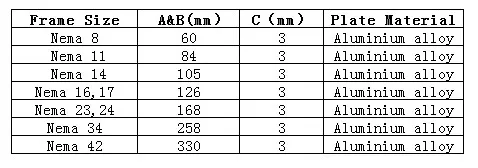
● Connect the motor to the appropriate heat sink according to the size of the motor base. A heat sink size table for each motor series can be found in the following figure:
 ● Through the heat sink, attach the motor to the bracket. The shaded area between the bracket and the heat sink is a nylon heat shield. Please refer to the following figure:
● Through the heat sink, attach the motor to the bracket. The shaded area between the bracket and the heat sink is a nylon heat shield. Please refer to the following figure:  ● Test the motor surface temperature by placing the sensor on the motor surface, driving the motor, and recording the results.
● Test the motor surface temperature by placing the sensor on the motor surface, driving the motor, and recording the results.