Introduction to Stepper Motors
A stepper motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical pulses into discrete mechanical movements. The shaft of a stepper motor rotates in discrete step increments when electrical command pulses are applied to it in the proper sequence.
Stepper motors are the most accessible devices for precise positioning control. They are widely used in various applications for position and speed via all kinds of control signals such as digital, analog, and communication.
Features
• Precise Positioning Control
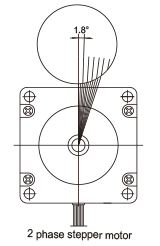
A stepper motor rotates with a fixed step angle, just like the second hand of a clock. This angle is called "basic step angle." MOONS' offers several types of "basic step angle" as standard motors: 2-phase stepping motors with a basic step angle of 0.9° and 1.8° and 3-phase stepping motors with a basic step angle of 1.2°.
Aside from the standard motor, MOONS' also offers stepper motors with other "basic step angle." These are 0.72°, 1.5°, 3.6°, and 3.75°. These motors are not listed in this catalog, please contact MOONS' for more information.
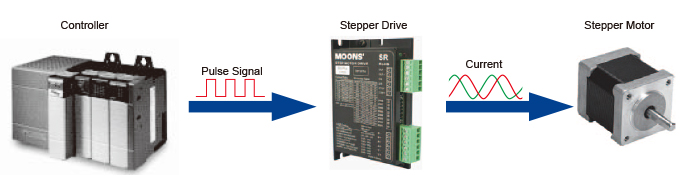
• Easy Control with Pulse Signals
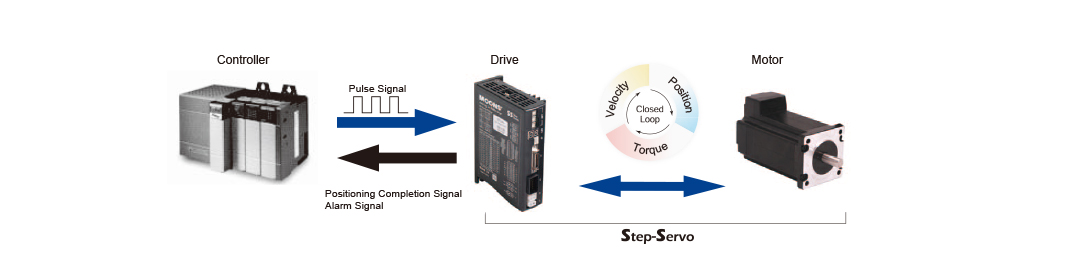
Below is a system configuration for high-accuracy positioning. Using pulse signals from the controller, the stepping motor's rotation angle and speed can be accurately controlled.
• What is a Pulse Signal?
An electrical pulse signal is a signal whose voltage level alternates between ON and OFF repeatedly. One pulse is counted for each ON/OFF cycle. With one pulse, the motor output shaft turns one step. Signal levels corresponding to voltage ON and OFF conditions are designated as "H" and "L."
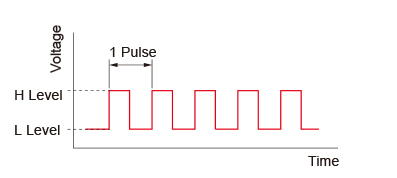
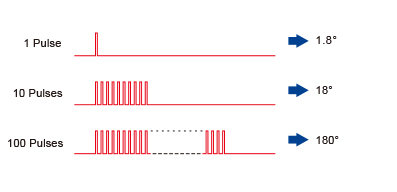
• The length of Rotation is Proportional to the Number of Pulses
The length of rotation of a stepping motor is proportional to the number of pulse signals (pulse number) given to the driver. A stepper motor's rotation (rotation angle of the motor output shaft) is related to pulse number as follows:

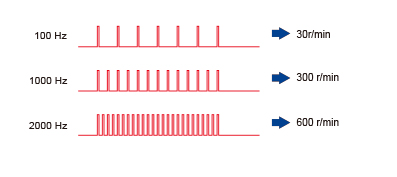
• The Speed is Proportional to the Pulse Frequency
Stepper motor speed is proportional to the frequency of pulse signals given to the driver. Following is the relationship between pulse frequency [Hz] and motor speed [r/min]:

• Generating High Torque with a Compact Size
In addition to generating high torque, stepper motors are compact in size. Their excellent acceleration and response make them ideal for torque-demanding applications where the motor must be started and stopped frequently. MOONS' also offers geared motors if greater torque is required at low speeds.
Frequent Starting/Stopping is Possible
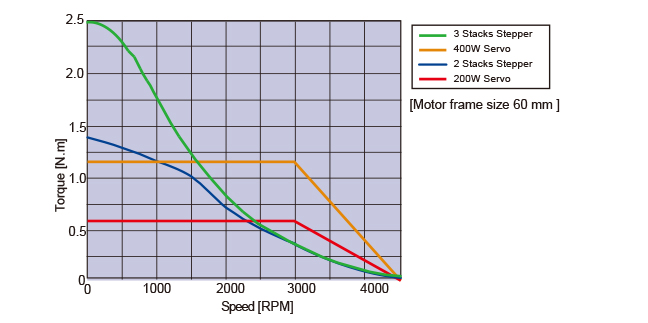
Speed VS Torque Characteristics comparetion between servo and stepper with same motor size.
• The Motor Holds Itself at a Stopped Position
When the windings are energized, the stepper motor has full torque at standstill. The motor can be held at a stopped position without using a mechanical brake.
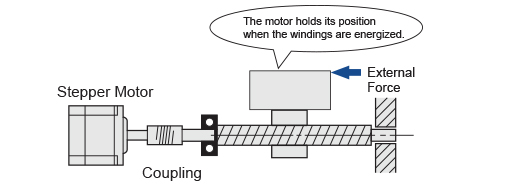
In vertical operations or when an external force is applied, the motor no longer holds the stopped position once the power is cut off, resulting in it losing its self-holding torque. Lifts and similar applications require electromagnetic brake motors.
In the world of stepping motors, the  is a technological revolution that combines stepping motors with servo technology to create an exceptional product.
is a technological revolution that combines stepping motors with servo technology to create an exceptional product.
 is a technological revolution that combines stepping motors with servo technology to create an exceptional product.
is a technological revolution that combines stepping motors with servo technology to create an exceptional product.Using the  , the performance is greatly improved to be much more Intelligent, Efficient, Compact, Accurate, Fast, and Smooth.
, the performance is greatly improved to be much more Intelligent, Efficient, Compact, Accurate, Fast, and Smooth.
 , the performance is greatly improved to be much more Intelligent, Efficient, Compact, Accurate, Fast, and Smooth.
, the performance is greatly improved to be much more Intelligent, Efficient, Compact, Accurate, Fast, and Smooth.
Stepper Motor Category
Stepper motors come in different types including the basic type, encoder type, IP65 type, Integrated type with drive and controller, brake type, and geared type. The availability of all options can also be combined together as the most optimized and compact motion control unit, for example, MOONS' can offer an encoder and geared type, IP65 integrated with drive, controller, and encoder, all combinations are available per request.
-
• Basic Type
 Easy-to-use and balanced model with a balanced set of features.
Easy-to-use and balanced model with a balanced set of features. -
• Encoder Type
 Encoder type stepper gives the possiblity for closed loop control, encoder feedback signals can be used for position verification and enhanced performance as stall detection and stall prevension depending on the features of the drive.
Encoder type stepper gives the possiblity for closed loop control, encoder feedback signals can be used for position verification and enhanced performance as stall detection and stall prevension depending on the features of the drive.
-
• IP65 Type
 In wet factory environments such as the food and beverage industries or outdoor applications, IP65-type stepper motors are ideal since they are dustproof and resistant to low pressure water jets.
In wet factory environments such as the food and beverage industries or outdoor applications, IP65-type stepper motors are ideal since they are dustproof and resistant to low pressure water jets.
IP65 specifies a product that is dust tight (no ingress of dust; complete protection against contact) and protected against water jets (water projected by a nozzle from any direction shall have no harmful effects). -
• Integrated Type with Drive and Controller
 Integrated stepper motors offer a space-saving design that reduces wiring and saves on cost over separate motor and drives components. For controller type, you only need a cable connection for Power and necessary communication or sensor depending on the application, it also costs for a host controller and makes it easy for you to set up a confiscated motion control system.
Integrated stepper motors offer a space-saving design that reduces wiring and saves on cost over separate motor and drives components. For controller type, you only need a cable connection for Power and necessary communication or sensor depending on the application, it also costs for a host controller and makes it easy for you to set up a confiscated motion control system.
-
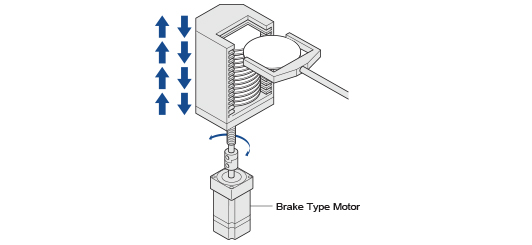
• Brake Type
 These motors incorporate a non-excitation type electromagnetic brake. When the power is accidentally cut off due to a power outage or other unexpected event, the electromagnetic brake holds the load in position to prevent it from dropping or moving. Brake-type steppers are wildly used in vertical axis applications.
These motors incorporate a non-excitation type electromagnetic brake. When the power is accidentally cut off due to a power outage or other unexpected event, the electromagnetic brake holds the load in position to prevent it from dropping or moving. Brake-type steppers are wildly used in vertical axis applications. -
• Geared Type
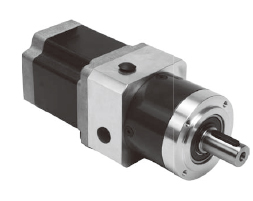 These motors incorporate a dedicated position-control gearhead with reduced backlash to make the most of the high controllability of the motors.
These motors incorporate a dedicated position-control gearhead with reduced backlash to make the most of the high controllability of the motors.
The gearhead ensures highly accurate, smooth operation even in applications where a large torque is received.
• Standard Hybrid Stepper Motor