Ball Screw Linear Actuator Product FAQs
1. What is repeatability? Answer: Repeatability refers to the consistency with which a slider returns to the same target position under a given set of conditions. For a C7-grade ball screw, the repeatability is ±0.01mm.  2. What is positioning accuracy? Answer: Positioning accuracy is the difference between the actual and theoretical positions when locating any point within the travel range, starting from the coordinate origin. Ball screw accuracy grades are generally classified as C0/C1/C2/C3/C5/C7/C10. For example, a C7-grade ball screw has a positioning error of ±0.05mm per 300mm of travel, while a C10-grade has an error of ±0.21mm per 300mm. 3. What is the maximum speed of MOONS' linear actuators? What is the wattage of the motors? Answer: As the speed of a stepper motor increases, its torque decreases. Therefore, when selecting a stepper motor, consider both speed and the available torque/thrust at that specific operating speed.
2. What is positioning accuracy? Answer: Positioning accuracy is the difference between the actual and theoretical positions when locating any point within the travel range, starting from the coordinate origin. Ball screw accuracy grades are generally classified as C0/C1/C2/C3/C5/C7/C10. For example, a C7-grade ball screw has a positioning error of ±0.05mm per 300mm of travel, while a C10-grade has an error of ±0.21mm per 300mm. 3. What is the maximum speed of MOONS' linear actuators? What is the wattage of the motors? Answer: As the speed of a stepper motor increases, its torque decreases. Therefore, when selecting a stepper motor, consider both speed and the available torque/thrust at that specific operating speed. 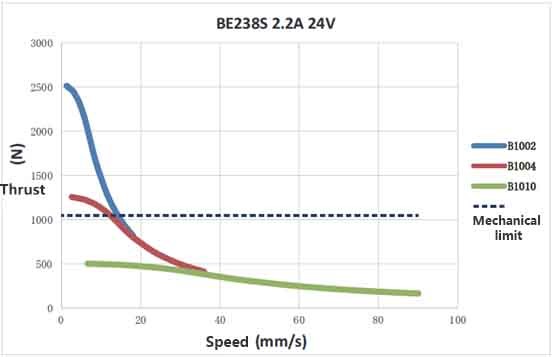 4. How can I resolve the issue of lost steps or stalling caused by insufficient thrust in a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: To resolve lost steps or stalling caused by insufficient thrust in a ball screw linear actuator, please check the following steps: First, verify that the drive current setting is close to the rated current of the motor. Second, check whether the motor starting frequency is too high and check whether the acceleration and deceleration settings are appropriate. Next, disable or power off the motor and manually rotate the leadscrew to move the nut through its full range. Verify that the leadscrew resistance torque is excessive and uniform. Then, loosen the nut mounting screws and manually push the load to ensure smooth movement without binding. If these steps do not reveal any issues, the product may be undersized for the application, a model with greater thrust should be selected. 5. How can I resolve the issue of excessive noise during operation of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: First, confirm whether the motor is operating in the low-speed resonance range, typically around 200pps. Second, install damping to isolate motor vibration. Use the anti-resonance, interpolation, or smoothing filtering features provided by the MOONS' drive can also effectively reduce noise. While ensuring the load is being driven, minimize the drive current. Using MOONS'-recommended grease not only helps reduce noise but also extends the life of the nut. For stepper servos or servo motors, check whether the PID parameters are set appropriately. If the noise persists after these checks, return the unit to the factory for inspection and repair. 6. How to solve the running vibration of ball screw linear actuator products? Answer: To resolve jitter in a ball screw actuator, please follow the steps below: First, if you are using a stepper servo product, confirm whether the PID parameters have been tuned. If it is an open-loop stepper, you can skip this step; second, replace the actuator with a known working unit to see if the jitter disappears. If the problem persists, the issue is likely with the driver or controller software settings; third, check the driver parameters to ensure they are set correctly; fourth, check the controller parameters to ensure they are set correctly. 7. How do I calculate the thrust of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: The calculation formula is as follows:
4. How can I resolve the issue of lost steps or stalling caused by insufficient thrust in a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: To resolve lost steps or stalling caused by insufficient thrust in a ball screw linear actuator, please check the following steps: First, verify that the drive current setting is close to the rated current of the motor. Second, check whether the motor starting frequency is too high and check whether the acceleration and deceleration settings are appropriate. Next, disable or power off the motor and manually rotate the leadscrew to move the nut through its full range. Verify that the leadscrew resistance torque is excessive and uniform. Then, loosen the nut mounting screws and manually push the load to ensure smooth movement without binding. If these steps do not reveal any issues, the product may be undersized for the application, a model with greater thrust should be selected. 5. How can I resolve the issue of excessive noise during operation of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: First, confirm whether the motor is operating in the low-speed resonance range, typically around 200pps. Second, install damping to isolate motor vibration. Use the anti-resonance, interpolation, or smoothing filtering features provided by the MOONS' drive can also effectively reduce noise. While ensuring the load is being driven, minimize the drive current. Using MOONS'-recommended grease not only helps reduce noise but also extends the life of the nut. For stepper servos or servo motors, check whether the PID parameters are set appropriately. If the noise persists after these checks, return the unit to the factory for inspection and repair. 6. How to solve the running vibration of ball screw linear actuator products? Answer: To resolve jitter in a ball screw actuator, please follow the steps below: First, if you are using a stepper servo product, confirm whether the PID parameters have been tuned. If it is an open-loop stepper, you can skip this step; second, replace the actuator with a known working unit to see if the jitter disappears. If the problem persists, the issue is likely with the driver or controller software settings; third, check the driver parameters to ensure they are set correctly; fourth, check the controller parameters to ensure they are set correctly. 7. How do I calculate the thrust of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: The calculation formula is as follows: 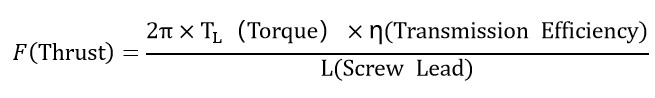 Ball screw efficiency is generally greater than 90%. Note: Thrust is calculated based on the motor's pull-out curve. The selection process must account for factors such as load inertia, acceleration, and mechanical friction. It is crucial to add a minimum 50% safety margin. 8. How do you calculate the self-locking force of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: The formula for calculating the self-locking force of a ball screw linear actuator is:
Ball screw efficiency is generally greater than 90%. Note: Thrust is calculated based on the motor's pull-out curve. The selection process must account for factors such as load inertia, acceleration, and mechanical friction. It is crucial to add a minimum 50% safety margin. 8. How do you calculate the self-locking force of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: The formula for calculating the self-locking force of a ball screw linear actuator is:  9. How is resolution calculated? Answer: Resolution is the axial distance (in mm) the slider moves for each full step of the motor. It is expressed in units of mm/full step. Formula: Resolution = Lead / (360° / Step Angle). Lead is the linear distance traveled by any point on a thread during one full rotation along the same helical line.
9. How is resolution calculated? Answer: Resolution is the axial distance (in mm) the slider moves for each full step of the motor. It is expressed in units of mm/full step. Formula: Resolution = Lead / (360° / Step Angle). Lead is the linear distance traveled by any point on a thread during one full rotation along the same helical line.
 2. What is positioning accuracy? Answer: Positioning accuracy is the difference between the actual and theoretical positions when locating any point within the travel range, starting from the coordinate origin. Ball screw accuracy grades are generally classified as C0/C1/C2/C3/C5/C7/C10. For example, a C7-grade ball screw has a positioning error of ±0.05mm per 300mm of travel, while a C10-grade has an error of ±0.21mm per 300mm. 3. What is the maximum speed of MOONS' linear actuators? What is the wattage of the motors? Answer: As the speed of a stepper motor increases, its torque decreases. Therefore, when selecting a stepper motor, consider both speed and the available torque/thrust at that specific operating speed.
2. What is positioning accuracy? Answer: Positioning accuracy is the difference between the actual and theoretical positions when locating any point within the travel range, starting from the coordinate origin. Ball screw accuracy grades are generally classified as C0/C1/C2/C3/C5/C7/C10. For example, a C7-grade ball screw has a positioning error of ±0.05mm per 300mm of travel, while a C10-grade has an error of ±0.21mm per 300mm. 3. What is the maximum speed of MOONS' linear actuators? What is the wattage of the motors? Answer: As the speed of a stepper motor increases, its torque decreases. Therefore, when selecting a stepper motor, consider both speed and the available torque/thrust at that specific operating speed.  4. How can I resolve the issue of lost steps or stalling caused by insufficient thrust in a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: To resolve lost steps or stalling caused by insufficient thrust in a ball screw linear actuator, please check the following steps: First, verify that the drive current setting is close to the rated current of the motor. Second, check whether the motor starting frequency is too high and check whether the acceleration and deceleration settings are appropriate. Next, disable or power off the motor and manually rotate the leadscrew to move the nut through its full range. Verify that the leadscrew resistance torque is excessive and uniform. Then, loosen the nut mounting screws and manually push the load to ensure smooth movement without binding. If these steps do not reveal any issues, the product may be undersized for the application, a model with greater thrust should be selected. 5. How can I resolve the issue of excessive noise during operation of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: First, confirm whether the motor is operating in the low-speed resonance range, typically around 200pps. Second, install damping to isolate motor vibration. Use the anti-resonance, interpolation, or smoothing filtering features provided by the MOONS' drive can also effectively reduce noise. While ensuring the load is being driven, minimize the drive current. Using MOONS'-recommended grease not only helps reduce noise but also extends the life of the nut. For stepper servos or servo motors, check whether the PID parameters are set appropriately. If the noise persists after these checks, return the unit to the factory for inspection and repair. 6. How to solve the running vibration of ball screw linear actuator products? Answer: To resolve jitter in a ball screw actuator, please follow the steps below: First, if you are using a stepper servo product, confirm whether the PID parameters have been tuned. If it is an open-loop stepper, you can skip this step; second, replace the actuator with a known working unit to see if the jitter disappears. If the problem persists, the issue is likely with the driver or controller software settings; third, check the driver parameters to ensure they are set correctly; fourth, check the controller parameters to ensure they are set correctly. 7. How do I calculate the thrust of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: The calculation formula is as follows:
4. How can I resolve the issue of lost steps or stalling caused by insufficient thrust in a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: To resolve lost steps or stalling caused by insufficient thrust in a ball screw linear actuator, please check the following steps: First, verify that the drive current setting is close to the rated current of the motor. Second, check whether the motor starting frequency is too high and check whether the acceleration and deceleration settings are appropriate. Next, disable or power off the motor and manually rotate the leadscrew to move the nut through its full range. Verify that the leadscrew resistance torque is excessive and uniform. Then, loosen the nut mounting screws and manually push the load to ensure smooth movement without binding. If these steps do not reveal any issues, the product may be undersized for the application, a model with greater thrust should be selected. 5. How can I resolve the issue of excessive noise during operation of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: First, confirm whether the motor is operating in the low-speed resonance range, typically around 200pps. Second, install damping to isolate motor vibration. Use the anti-resonance, interpolation, or smoothing filtering features provided by the MOONS' drive can also effectively reduce noise. While ensuring the load is being driven, minimize the drive current. Using MOONS'-recommended grease not only helps reduce noise but also extends the life of the nut. For stepper servos or servo motors, check whether the PID parameters are set appropriately. If the noise persists after these checks, return the unit to the factory for inspection and repair. 6. How to solve the running vibration of ball screw linear actuator products? Answer: To resolve jitter in a ball screw actuator, please follow the steps below: First, if you are using a stepper servo product, confirm whether the PID parameters have been tuned. If it is an open-loop stepper, you can skip this step; second, replace the actuator with a known working unit to see if the jitter disappears. If the problem persists, the issue is likely with the driver or controller software settings; third, check the driver parameters to ensure they are set correctly; fourth, check the controller parameters to ensure they are set correctly. 7. How do I calculate the thrust of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: The calculation formula is as follows: 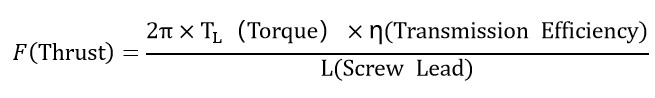 Ball screw efficiency is generally greater than 90%. Note: Thrust is calculated based on the motor's pull-out curve. The selection process must account for factors such as load inertia, acceleration, and mechanical friction. It is crucial to add a minimum 50% safety margin. 8. How do you calculate the self-locking force of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: The formula for calculating the self-locking force of a ball screw linear actuator is:
Ball screw efficiency is generally greater than 90%. Note: Thrust is calculated based on the motor's pull-out curve. The selection process must account for factors such as load inertia, acceleration, and mechanical friction. It is crucial to add a minimum 50% safety margin. 8. How do you calculate the self-locking force of a ball screw linear actuator? Answer: The formula for calculating the self-locking force of a ball screw linear actuator is:  9. How is resolution calculated? Answer: Resolution is the axial distance (in mm) the slider moves for each full step of the motor. It is expressed in units of mm/full step. Formula: Resolution = Lead / (360° / Step Angle). Lead is the linear distance traveled by any point on a thread during one full rotation along the same helical line.
9. How is resolution calculated? Answer: Resolution is the axial distance (in mm) the slider moves for each full step of the motor. It is expressed in units of mm/full step. Formula: Resolution = Lead / (360° / Step Angle). Lead is the linear distance traveled by any point on a thread during one full rotation along the same helical line. 